2. User Interface
The UI (User Interface)
2.1 Dashboard
The dashboard is your personalized homepage, offering an overview of information and quick access to features. Upon signing in, you will be directed to your default dashboard, which can be customized. Dashboards typically contain sections or widgets displaying data, charts, graphs, or lists. You can customize your dashboard by adding, removing, or rearranging sections. Clicking on a section or widget can provide detailed information or launch related functionality.\
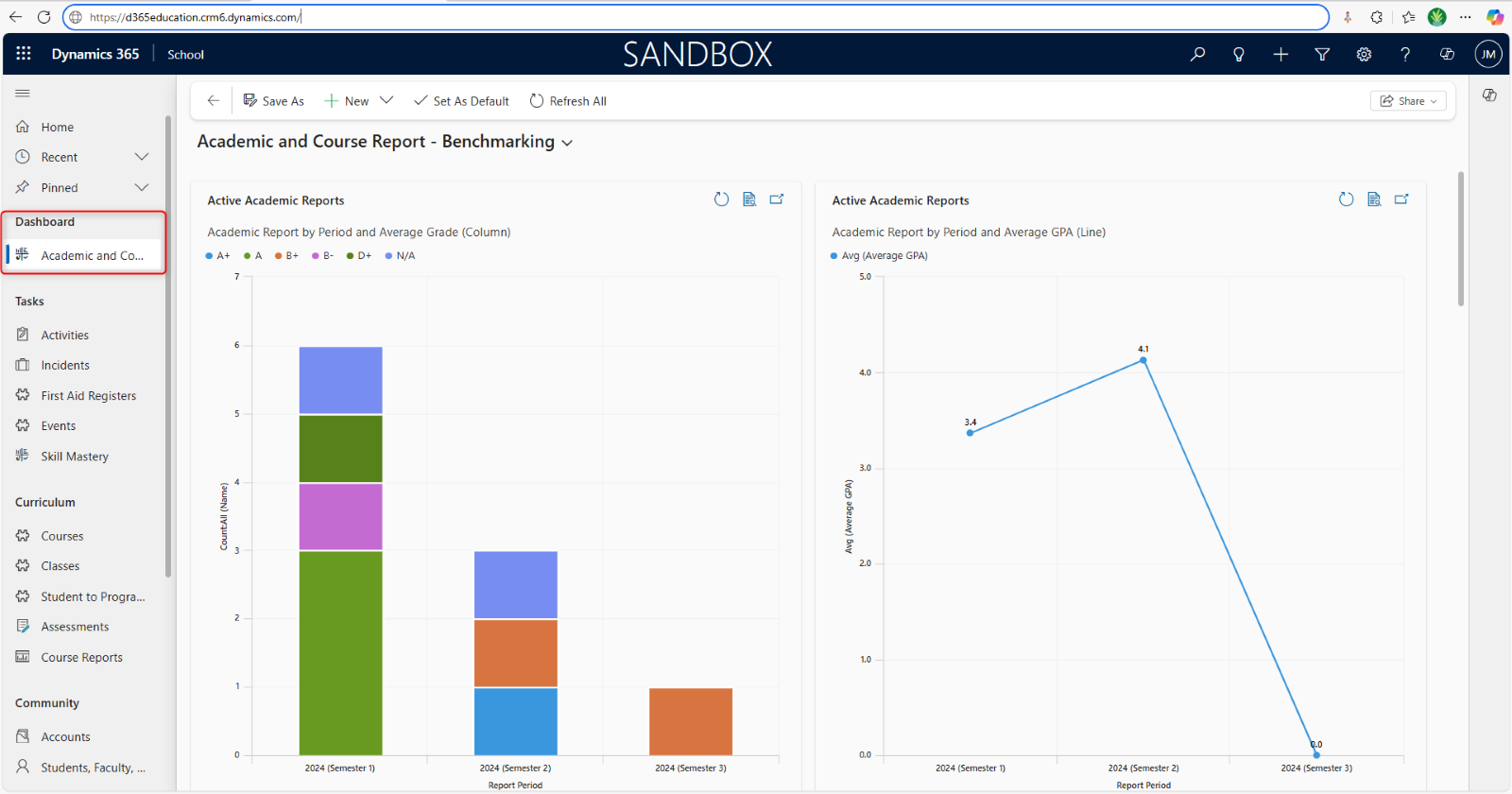
Your dashboard is a powerful and highly customizable data visualization tool that provides a centralized, at-a-glance overview of key business information. Think of it as your personal control panel or mission control center for your specific role or area of responsibility within the system. On the left-hand side of your dashboard are menu options for quick and easy access to Dynamics 365 module features. Select what you need to access, and it will appear in the display as a View.
2.2. Views and Filters
Views and filters help organize and customize data displayed in lists and grids. These represent how data is displayed in your view. Within a module, switch between different views to display data in specific formats. Views can be predefined or personalized. Use filters to refine displayed data by specifying a criterion (e.g., date ranges, status). Save and apply filters for future use or share them with other users.
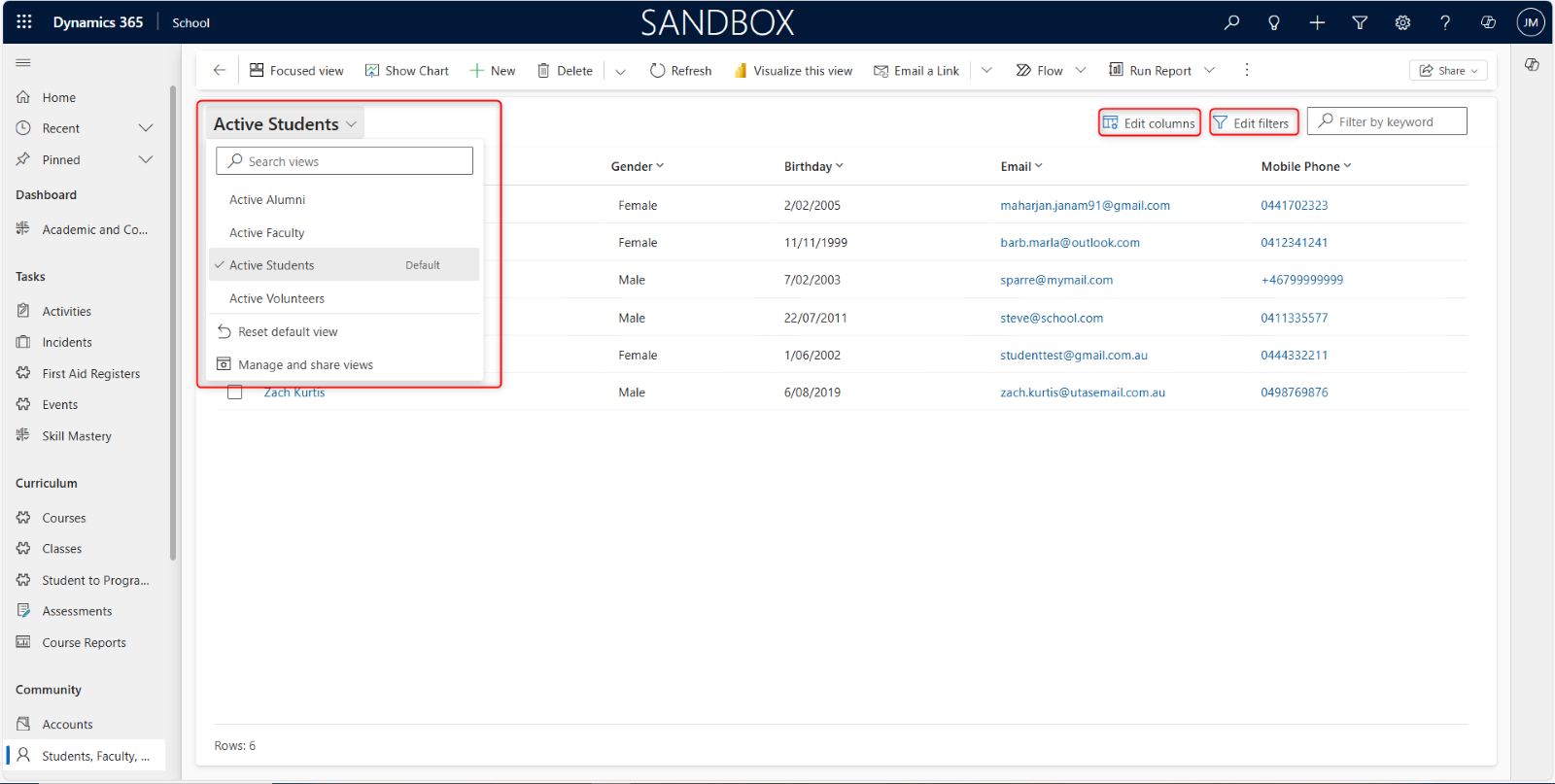
Views appear inside your Dynamics 365 dashboard. For example, in the image above, you can see the Active Opportunities view with a search box to query for information. To the right you can see the Edit Columns and Edit Filters button. Columns are the data stored for a particular view, like Active Opportunities. Filters are how you want to view the data, based on a criterion which you can specify using Filter by keyword. Type your keyword and hit enter on your keyboard to display the view.
2.3. Tabs and Sections
Tabs and sections organize information within forms or records.
-
Tabs: Horizontal navigation elements that divide a form into distinct, related sections.
-
Sections: Further organize fields and data within each tab.
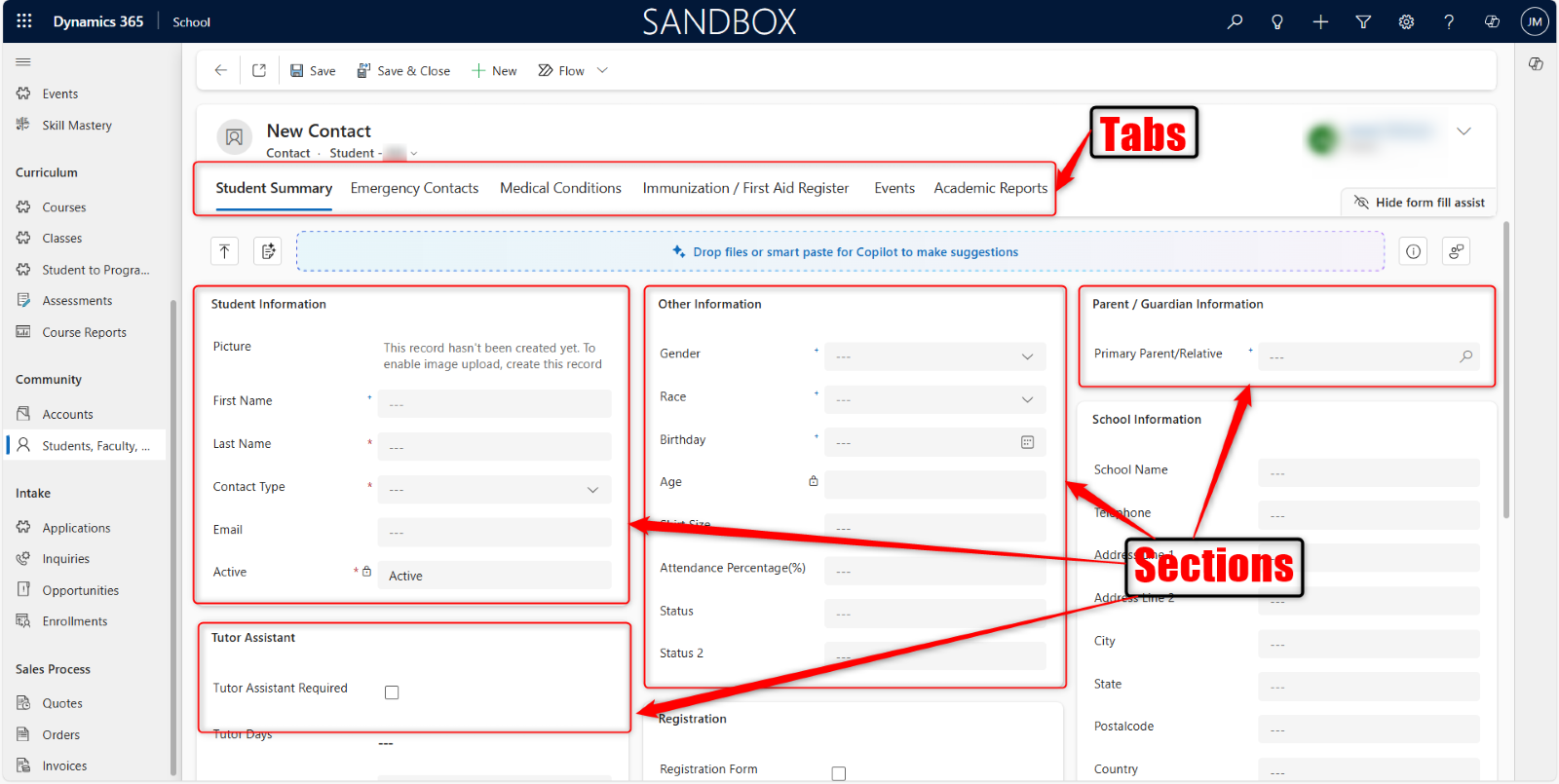
When you click a tab, it opens a view. In the above example you can see tabs that represent Student Summary. It opens a view that is divided into sections, which display specific information.
2.4. Field Types and Input Controls
Dynamics 365 supports various field types for data entry and input control. Fields accept data input from users.
Text Fields: For alphanumeric characters and strings (names, addresses, descriptions). Text input is between 100 to 255 characters long.
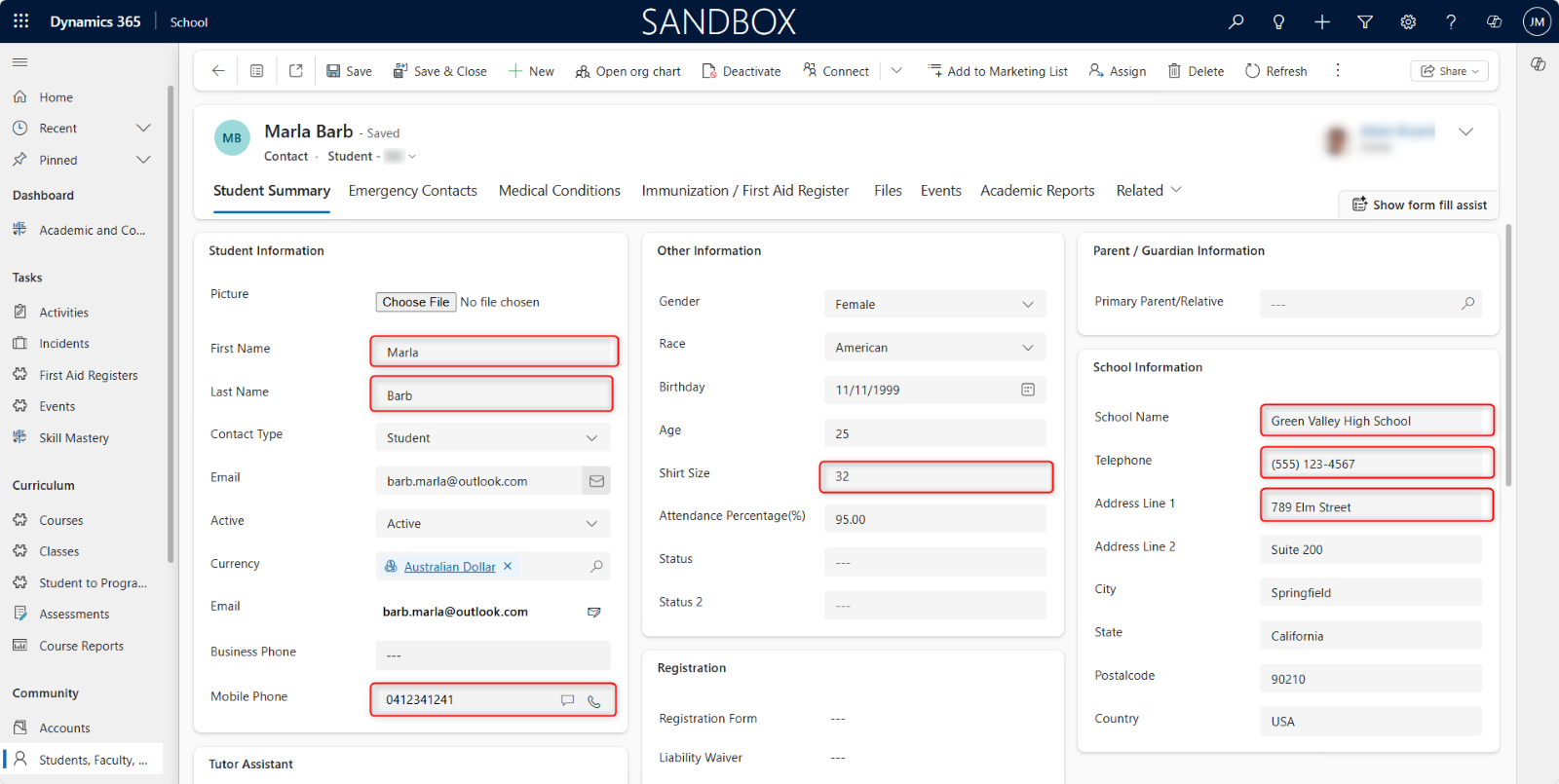
These are among the most common field types you will encounter when managing records like Contacts, Accounts, Opportunities, Inquiries, Enrollments, and any custom entities.
Text fields provide the data captured in Dynamics 365. From the text fields, the data is processed into the information made available for the School environment users.
Drop-down Lists: Provide predefined options for selection, ensuring consistency.
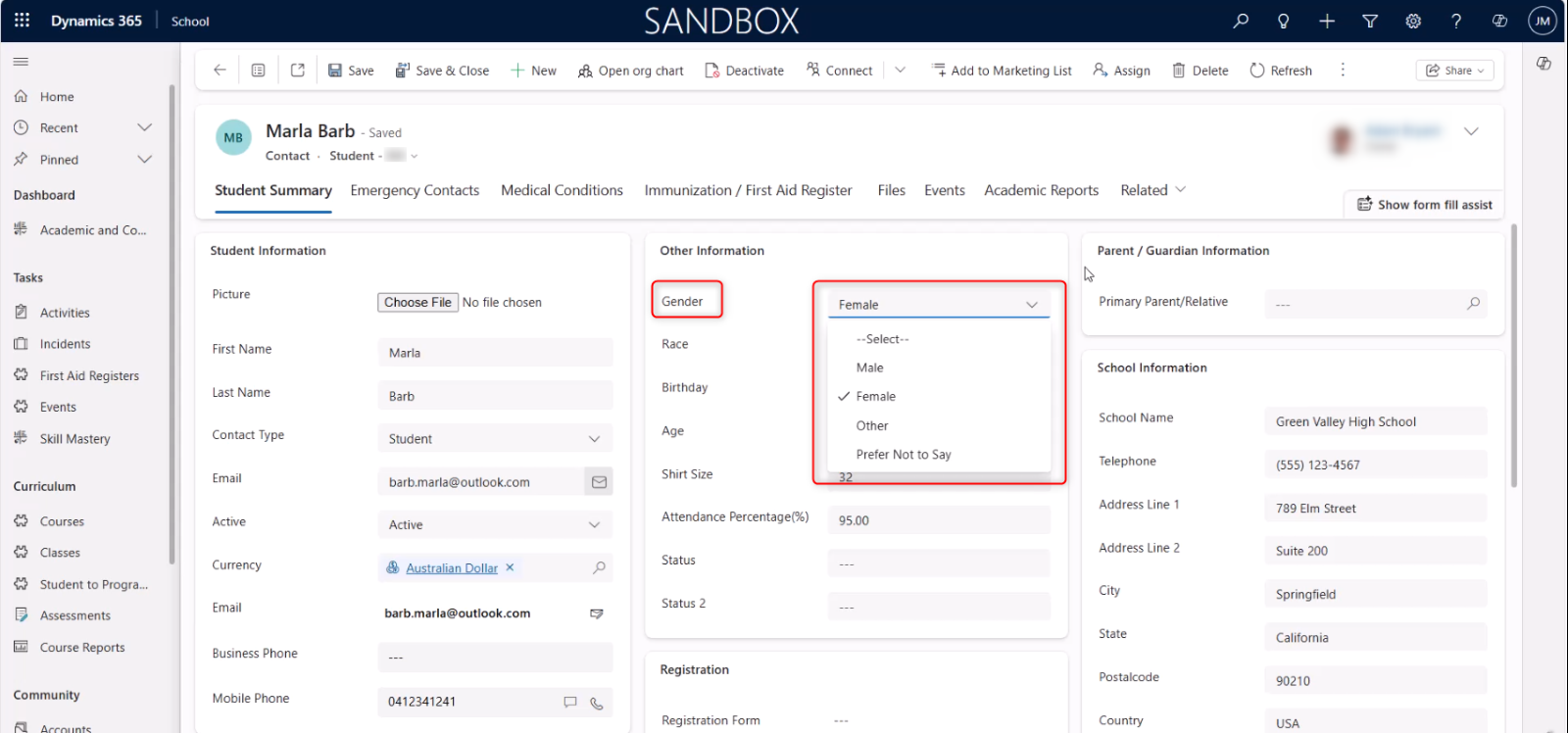
A drop-down list (also called drop-down box) provides a pre-defined list of items for users to choose from. Only one option can be selected, and not all items can be selected.
With pre-defined choices, it is easier and faster to add values to a field. You can only use the choices provided, and you cannot add your own value.
Checkboxes: For binary (true/false, yes/no) choices.
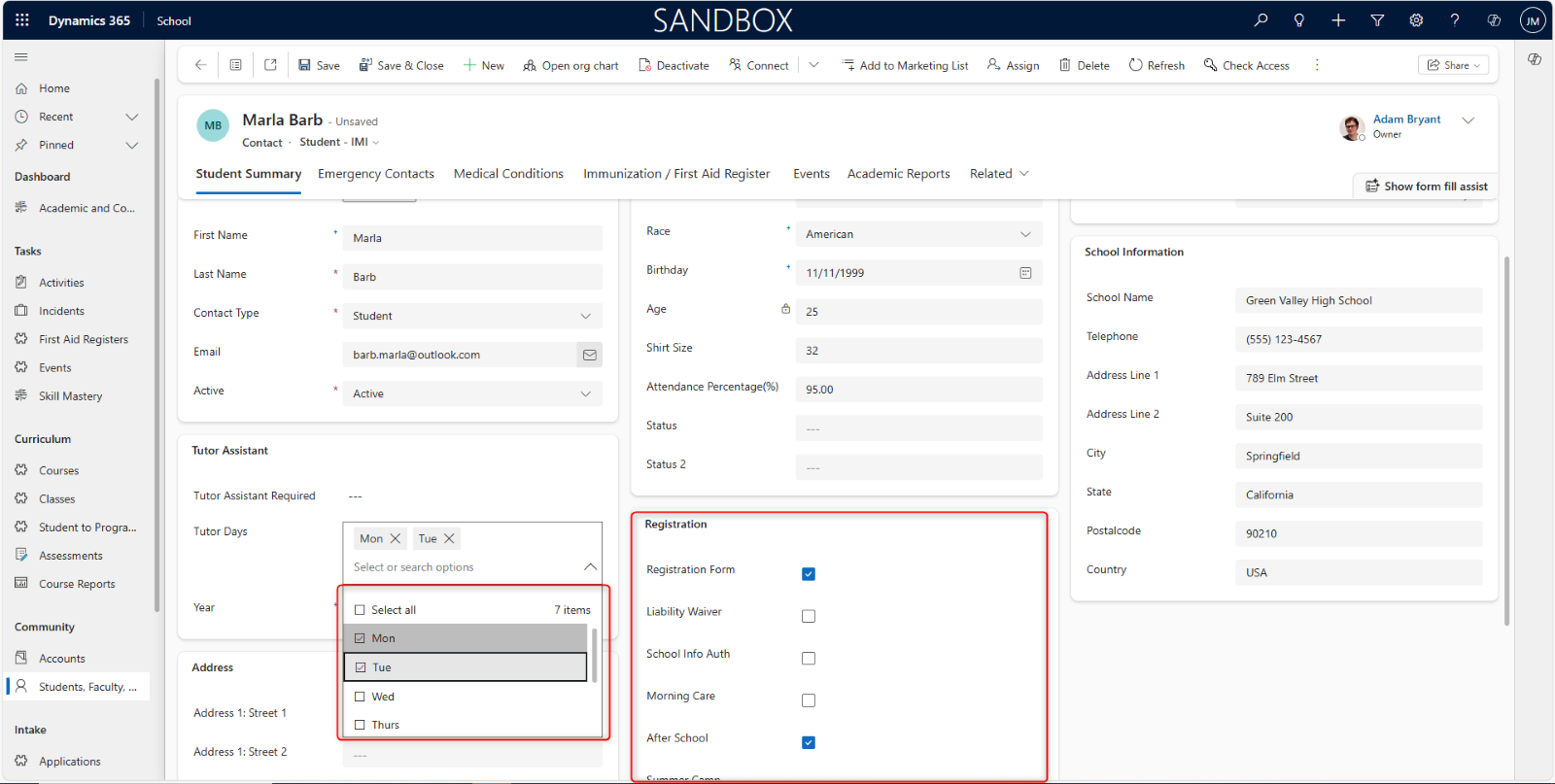
A check indicates a yes or true value. If a box is not checked, it indicates a no or false value.
You can have multiple checkboxes. Depending on the condition, you can check as many boxes as applicable to you. You might also be allowed to select all checkboxes, if it is allowed.
Date pickers: Facilitate selecting dates from a calendar.
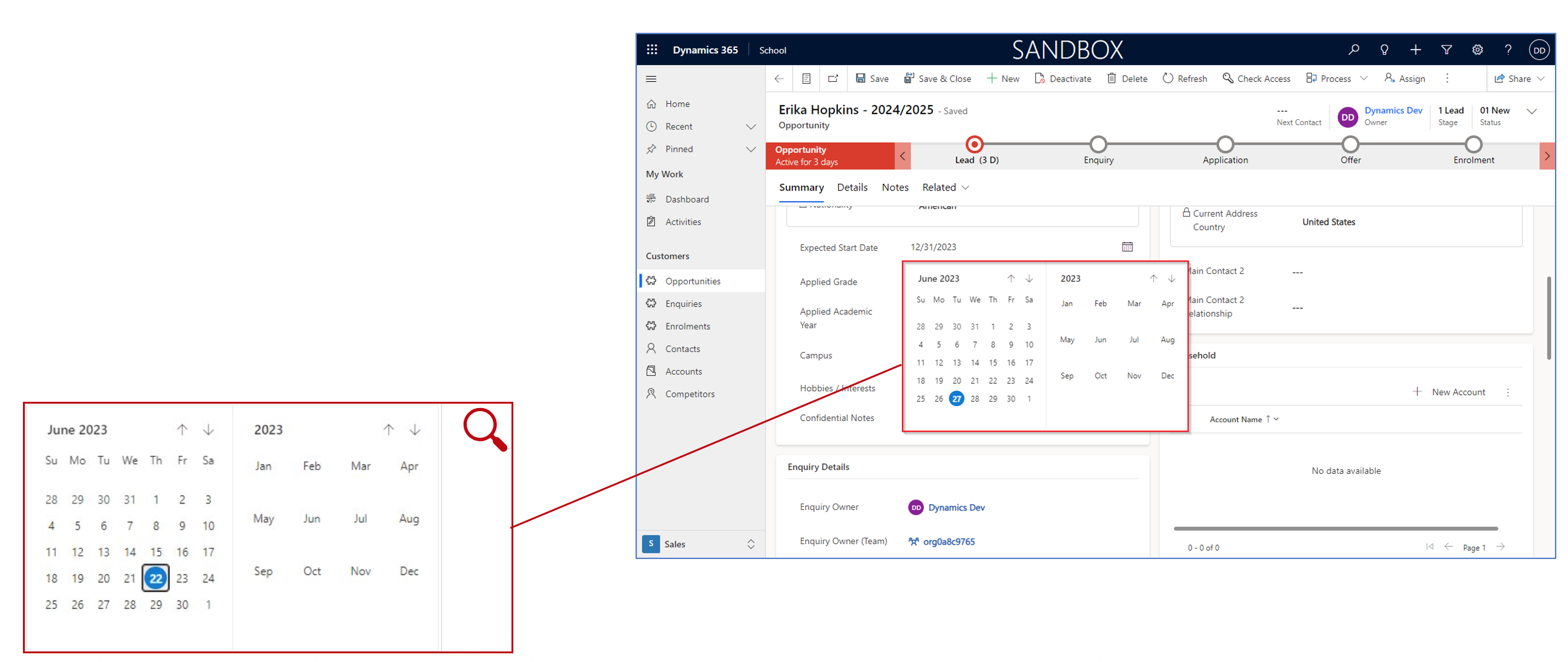
This field type is used to store specific points in time, either a date only, or both a date and a time. You will be provided with a calendar box from where you can select the date and time you want.
Numeric Fields: For numerical values (quantities, grades).
Numeric fields are specifically designed for numbers only, enabling mathematical operations, sorting, and specific validation rules. It can store very large positive or negative whole numbers (typically from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647).
You cannot input characters or symbols in a numeric field. This field is commonly used for storing data like phone numbers, student ID, accounts, grades, and student age.
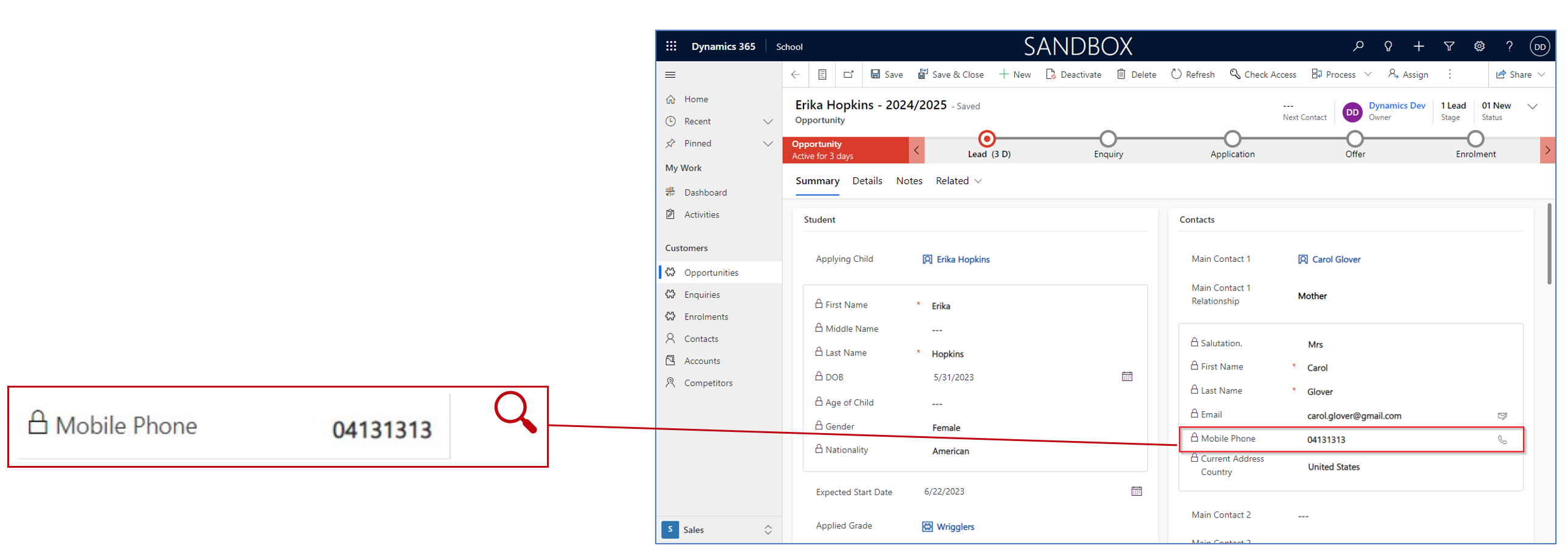
Lookup Fields: Allow searching for and linking to related records.
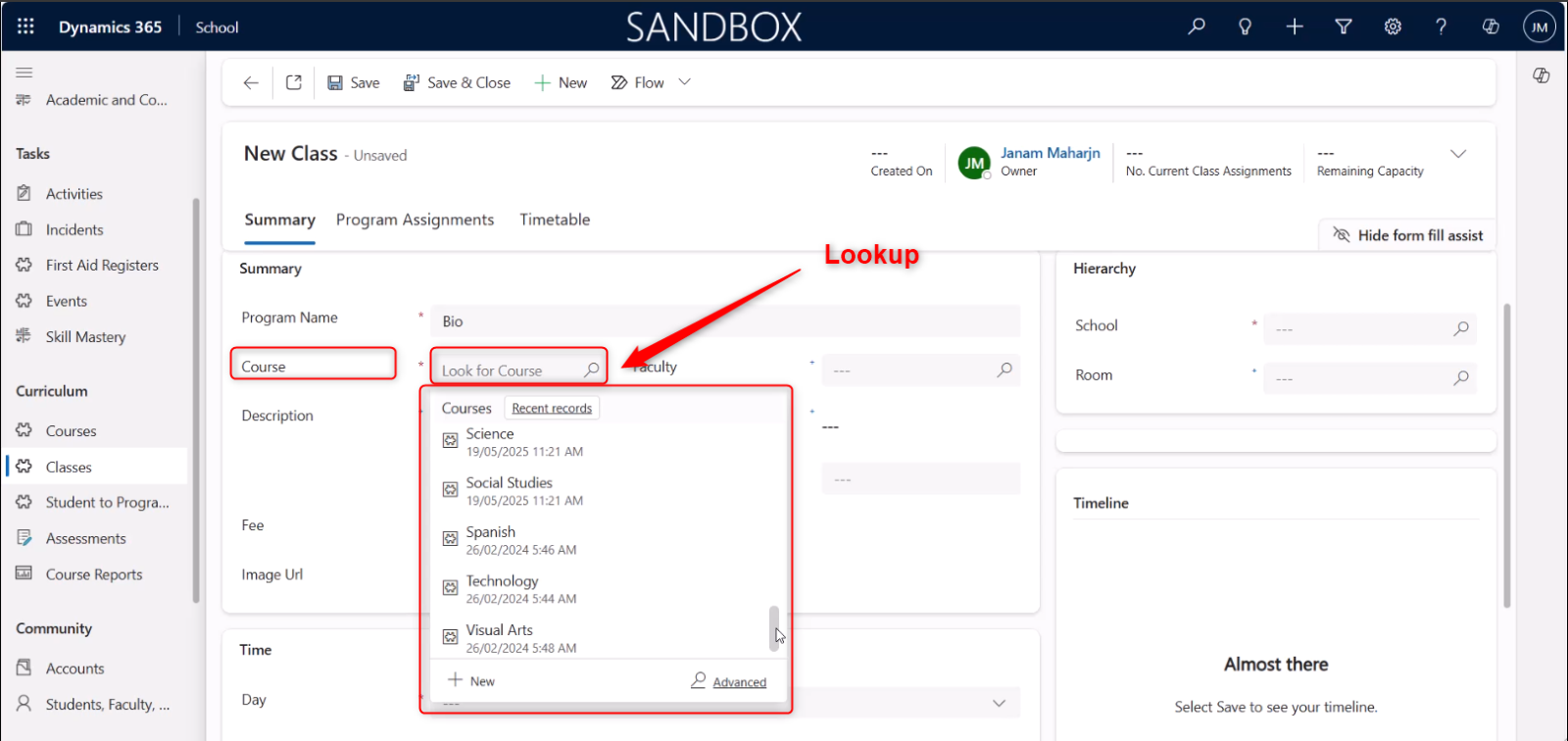
The lookup data type is used to create relationships between different records or entities. Essentially, it allows you to link one record to another existing record within the Dynamics 365 system.
For example, “This Opportunity is linked to that specific Account,” or “This Contact is related to that specific Company.”